In our December Night Sky Notes, we mentioned that the Orion constellation has a distinct hourglass shape that makes it easy to spot in the night sky. But what if we told you that this is not the complete constellation, but rather, an asterism?
An asterism is a pattern of stars in the night sky, forming shapes that make picking out constellations easy. Cultures throughout history have created these patterns as part of storytelling, honoring ancestors, and timekeeping. Orion’s hourglass is just one of many examples of this, but did you know Orion’s brightest knee is part of another asterism that spans six constellations, weaving together the Winter night sky? Many asterisms feature bright stars that are easily visible to the naked eye. Identify these key stars, and then connect the dots to reveal the shape.
Asterisms Through the Seasons
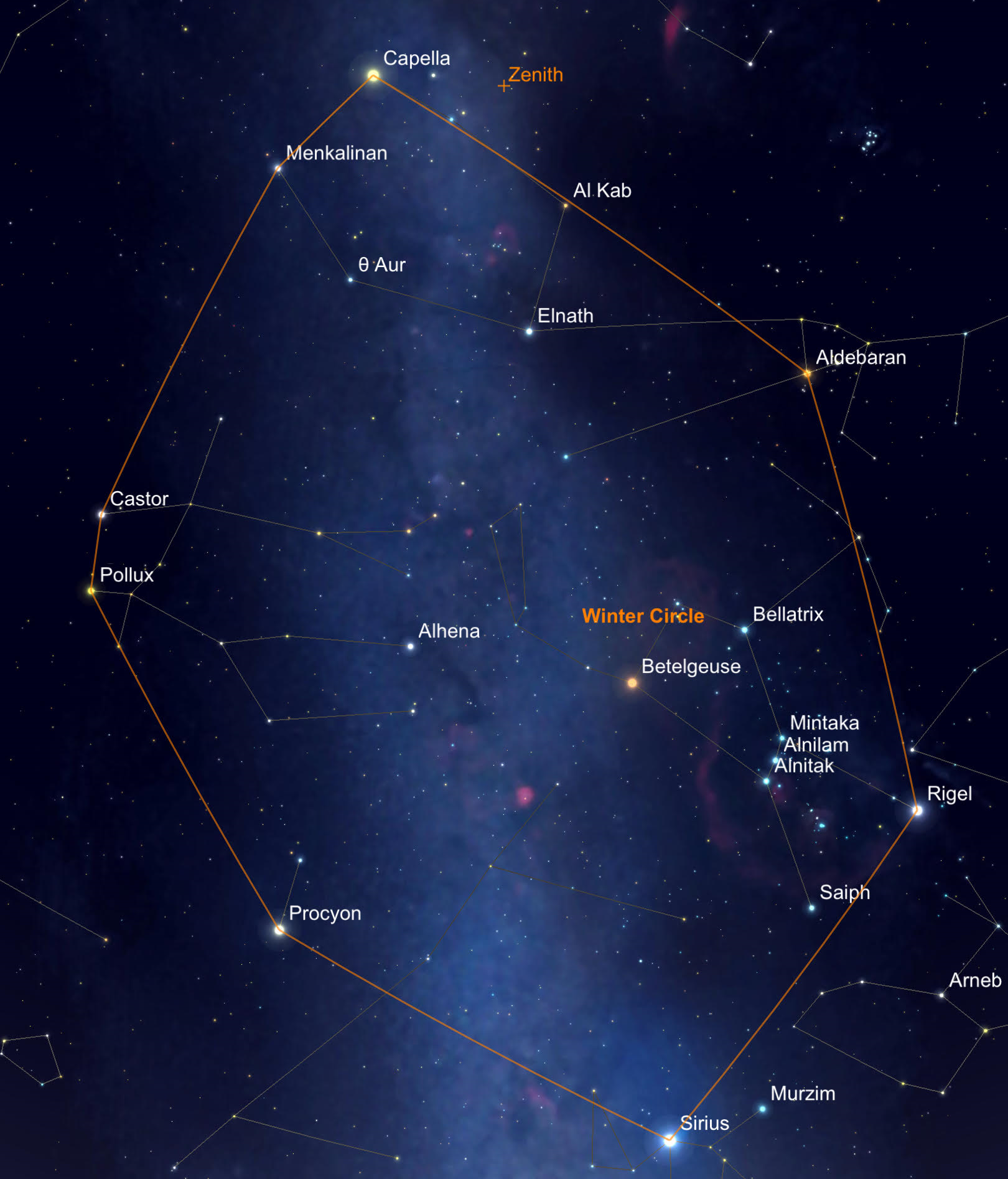
Stars that make up the Winter Circle, as seen on January 1, 2024
Sky Safari
Try looking for these asterisms this season and beyond:
- Winter Circle – this asterism, also known as the Winter Hexagon, makes up a large portion of the Winter sky using stars Rigel, Aldebaran, Capella, Pollux, Procyon, and Sirius as its points. Similarly, the Winter Triangle can be found using Procyon, Sirius, and Betelgeuse as points. Orion’s Belt is also considered an asterism.
- Diamond of Virgo – this springtime asterism consists of the following stars: Arcturus, in the constellation Boötes; Cor Caroli, in Canes Venatici; Denebola in Leo, and Spica in Virgo. Sparkling at the center of this diamond is the bright cluster Coma Berenices, or Bernice’s Hair – an ancient asterism turned constellation!
- Summer Triangle – as the nights warm up, the Summer Triangle dominates the heavens. Comprising the bright stars Vega in Lyra, Deneb in Cygnus, and Altair in Aquila, this prominent asterism is the inspiration behind the cultural festival Tanabata. Also found is Cygnus the Swan, which makes up the Northern Cross
- Great Square of Pegasus – by Autumn, the Great Square of Pegasus can be seen. This square-shaped asterism takes up a large portion of the sky, and consists of the stars: Scheat, Alpheratz, Markab and Algenib.
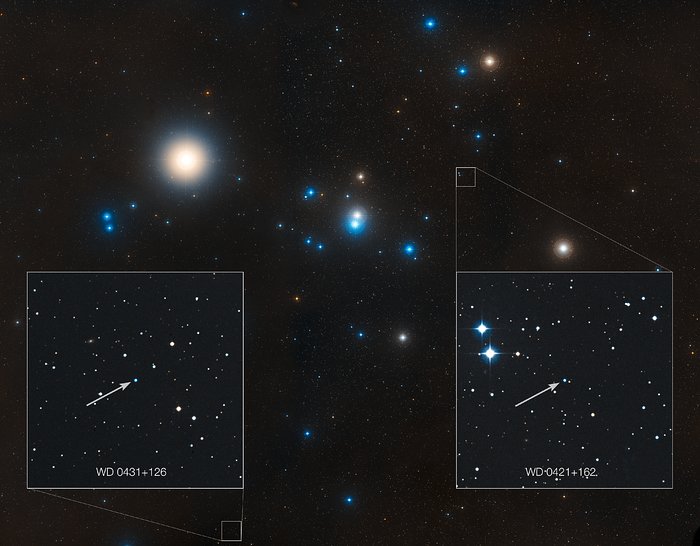

This image shows the region around the Hyades star cluster, the nearest open cluster to us. The Hyades cluster is very well-studied due to its location, but previous searches for planets have produced only one. A new study led by Jay Farihi of the University of Cambridge, UK, has now found the atmospheres of two burnt-out stars in this cluster — known as white dwarfs — to be “polluted” by rocky debris circling the star. Inset, the locations of these white dwarf stars are indicated — stars known as WD 0421+162, and WD 0431+126.
This image shows the region around the Hyades star cluster, the nearest open cluster to us. The Hyades cluster is very well-studied due to its location, but previous searches for planets have produced only one. A new study led by Jay Farihi of the University of Cambridge, UK, has now found the atmospheres of two burnt-out stars in this cluster — known as white dwarfs — to be “polluted” by rocky debris circling the star. Inset, the locations of these white dwarf stars are indicated — stars known as WD 0421+162, and WD 0431+126.
NASA, ESA, STScI, and Z. Levay (STScI)
Tracing these outlines can guide you to objects like galaxies and star clusters. The Hyades, for example, is an open star cluster in the Taurus constellation with evidence of rocky planetary debris. In 2013, Hubble Space Telescope’s Cosmic Origins Spectrograph was responsible for breaking down light into individual components. This observation detected low levels of carbon and silicon – a major chemical for planetary bodies. The Hyades can be found just outside the Winter Circle and is a favorite of both amateur and professional astronomers alike.
How to Spot Asterisms
- Use Star Maps and Star Apps – Using star maps or stargazing apps can help familiarize yourself with the constellations and asterisms of the night sky.
- Get Familiar with Constellations – Learning the major constellations and their broader shapes visible each season will make spotting asterisms easier.
- Use Celestial Landmarks – Orient yourself by using bright stars, or recognizable constellations. This will help you navigate the night sky and pinpoint specific asterisms. Vega in the Lyra constellation is a great example of this.
Learn more about how to stay warm while observing this Winter with our upcoming mid-month article on the Night Sky Network page through NASA’s website!
This article is distributed by NASA’s Night Sky Network (NSN).
The NSN program supports astronomy clubs across the USA dedicated to astronomy outreach. Visit nightsky.jpl.nasa.gov to find local clubs, events, and more!